January 08, 2020
Wednesday, January 8, 2020
Monday, August 5, 2019
Monday, April 1, 2019
Cloud-Computing
April 01, 2019
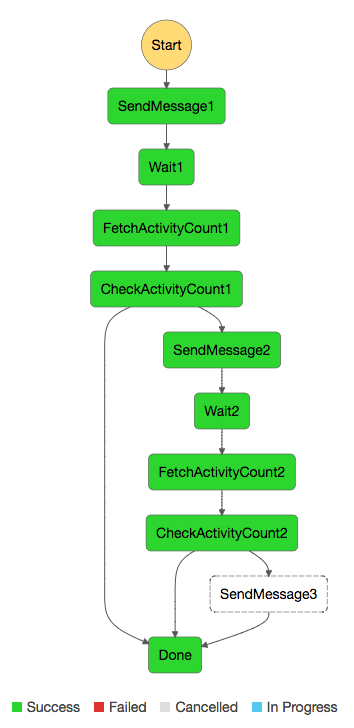
What is AWS Step Functions?
AWS Step Functions is a web service that enables you to coordinate the components of distributed applications and microservices using visual workflows. You build applications from individual components that each perform a discrete function, or task, allowing you to scale and change applications quickly. Step Functions provides a reliable way to coordinate components and step through the functions of your application. Step Functions provides a graphical console to visualize the components of your application as a series of steps. It automatically triggers and tracks each step, and retries when there are errors, so your application executes in order and as expected, every time. Step Functions logs the state of each step, so when things do go wrong, you can diagnose and debug problems quickly Learn AWS Certification Training.
Step Functions manages the operations and underlying infrastructure for you to ensure your application is available at any scale.
You can run your tasks on the AWS Cloud, on your own servers, or on any system that has access to AWS. AWS Online Training will Guide the Step Functions can be accessed and used with the Step Functions console, the AWS SDKs, or an HTTP API. This guide shows you how to develop, test, and troubleshoot your own state machine using these methods.
Overview of Step Functions:
Here are some of the key features of AWS Step Functions:
- Step Functions is based on the concepts of tasks and state machines
- You define state machines using the JSON-based Amazon States Language
- The Step Functions console displays a graphical view of your state machine’s structure, which provides you with a way to visually check your state machine’s logic and monitor executions.
Supported Regions:
Currently, Step Functions is supported only in the following regions:
- US East (Ohio)
- US East (N. Virginia)
- US West (Oregon)
- Asia Pacific (Sydney)
- Asia Pacific (Tokyo)
- EU (Frankfurt)
- EU (Ireland)
- EU (London)
About Amazon Web Services:
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a collection of digital infrastructure services that developers can leverage when developing their applications. The services include computing, storage, database, and application synchronization (messaging and queuing). AWS uses a pay-as-you-go service model: you are charged only for the services that you — or your applications — use. For new AWS users, a free usage tier is available. On this tier, services are free below a certain level of usage. For more information about AWS costs and the Free Tier, see Use the AWS Free Tier. To obtain an AWS account, visit the AWS home page and choose to Create a Free Account.
Sunday, March 31, 2019
Cloud-Computing
March 31, 2019
AWS ─ Cloud Computing
In 2006, Amazon Web Services (AWS) started to offer IT services to the market in the form of web services, which is nowadays known as cloud computing. With this cloud, we need not plan for servers and other IT infrastructure which takes up much of time in advance. Instead, these services can instantly spin up hundreds or thousands of servers in minutes and deliver results faster. We pay only for what we use with no up-front expenses and no long-term commitments, which makes AWS cost efficient. Today, AWS provides a highly reliable, scalable, low-cost infrastructure platform in the cloud that powers a multitude of businesses in 190 countries around the world. For more Learn AWS Certification Training.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is Internet-based computing in which large groups of remote servers are networked to allow centralized data storage and learn online training to computer services or resources.
There are several other broadly accepted definitions of cloud computing. Some explicitly emphasize reconfigurability of the resources, while others include the need for rapid on-demand provisioning of resources, and still, others drop the requirement of access via the internet. We define cloud computing as a model that enables the features listed here:
- Users should be able to provision and release resources on-demand
- The resources can be scaled up or down automatically, depending on the load
- The provisioned resources should be accessible over a network
- Cloud service providers should enable a pay-as-you-go model, where customers are charged based on the type and quantum of resources they consume.
There are three types of clouds - Public, Private, and Hybrid cloud.
Public Cloud:
Public Cloud:
In the public cloud, third-party service providers make resources and services available to their customers via the Internet. Customer’s data and related security are with the service providers’ owned infrastructure.
Private Cloud:
A private cloud also provides almost similar features as a public cloud, but the data and services are managed by the organization or by the third party only for the customer’s organization. In this type of cloud, major control is over the infrastructure so security-related issues are minimized.
Hybrid Cloud:
A hybrid cloud is the combination of both private and public cloud. The decision to run on private or public cloud usually depends on various parameters like the sensitivity of data and applications, industry certifications and required standards, regulations, etc.
Cloud Service Models:
There are three types of service models in cloud - IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
IaaS:
IaaS stands for Infrastructure as a Service. It provides users with the capability to provision processing, storage, and network connectivity on demand. Using this service model, the customers can develop their own applications on these resources.
PaaS:
PaaS stands for Platform as a Service. Here, the service provider provides various services like databases, queues, workflow engines, e-mails, etc. to their customers. The customer can then use these components for building their own applications. The services, availability of resources and data backup are handled by the service provider that helps the customers to focus more on their application's functionality.
SaaS:
SaaS stands for Software as a Service. As the name suggests, here the third-party providers provide end-user applications to their customers with some administrative capability at the application level, such as the ability to create and manage their users. Also, some level of customizability is possible such as the customers can use their own corporate logos, colours, etc.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Here is a list of some of the most important advantages that Cloud Computing has to offer:
- Cost-Efficient: Building our own servers and tools is time-consuming as well as expensive as we need to order, pay for, install, and configure expensive hardware, long before we need it. However, using cloud computing, we only pay for the amount we use and when we use the computing resources. In this manner, you learn AWS Online Training with cloud computing.
- Reliability: A cloud computing platform provides much more managed, reliable and consistent service than an in-house IT infrastructure. It guarantees 24x7 and 365 days of service. If any of the servers fails, then hosted applications and services can easily be transited to any of the available servers.
- Unlimited Storage: Cloud computing provides almost unlimited storage capacity, i.e., we need not worry about running out of storage space or increasing our current storage space availability. We can access as much or as little as we need.
- Backup & Recovery: Storing data in the cloud, backing it up and restoring the same is relatively easier than storing it on a physical device. The cloud service providers also have enough technology to recover our data, so there is the convenience of recovering our data anytime.
- Easy Access to Information: Once you register yourself in a cloud, you can access your account from anywhere in the world provided there is internet connection at that point. There are various storage and security facilities that vary with the account type chosen.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Although Cloud Computing provides a wonderful set of advantages, it has some drawbacks as well that often raise questions about its efficiency.
- Security issues: Security is a major issue in cloud computing. The cloud service providers implement the best security standards and industry certifications, however, storing data and important files on external service providers always bears a risk. AWS cloud infrastructure is designed to be the most flexible and secure cloud network. It provides a scalable and highly reliable platform that enables customers to deploy applications and data quickly and securely.
- Technical issues: As cloud service providers offer services to a number of clients each day, sometimes the system can have some serious issues leading to business processes temporarily being suspended. Additionally, if the internet connection is offline then we will not be able to access any of the applications, server, or data from the cloud.
- Not easy to switch service providers: Cloud service providers promise vendors that the cloud will be flexible to use and integrate, however switching cloud services is not easy. Most organizations may find it difficult to host and integrate current cloud applications on another platform. Interoperability and support issues may arise such as applications developed on the Linux platform may not work properly on Microsoft Development Framework (.Net).
Tuesday, March 5, 2019
Cloud-Computing
March 05, 2019
AWS Basics
1. What is AWS:
Amazon Web Services, popularly known as AWS, is a comprehensive and secure cloud services platform provided by Amazon. The AWS Cloud or Amazon cloud offers a good range of infrastructure services, like storage options, computing power, networking and databases to businesses, helping them scale and grow. Amazon delivers its services on-demand with pay-as-you-go rating policy. For more Learn AWS Online Training
2. AWS - Basic Architecture:
This is the basic structure of AWS EC2, wherever EC2 stands for Elastic Compute Cloud. EC2 enables users to use virtual machines of various configurations as per their requirement. It allows various configuration choices, mapping of an individual server, various rating options, etc. we'll discuss these in detail in AWS products section. Following is that the diagrammatic representation of the architecture.
3. AWS - Management Console:
The AWS Management Console is a browser-based GUI for Amazon Web Services (AWS). Through the console, a client will manage their cloud computing, cloud storage and different resources running on the Amazon Web Services infrastructure. Our AWS Training Well Guide an AWS.

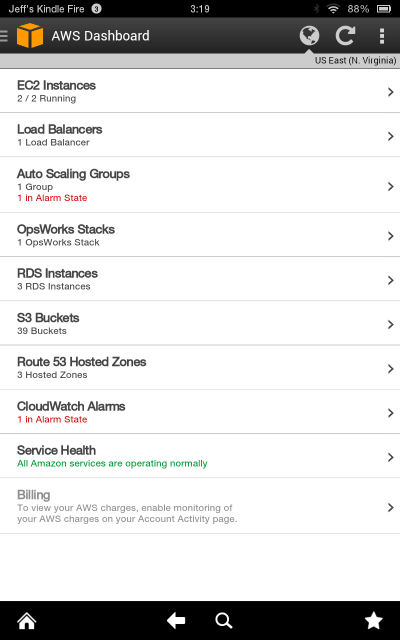
4. AWS - Console Mobile App:
iOS users can currently monitor and access their AWS resources through the new AWS Console mobile application. The Dashboard provides allowable users with a single read a resource's status, with time period knowledge on Amazon Cloud Watch, Personal Health Dashboard, and AWS billing and Cost Management.
5. AWS – Account:
1. Create your account:
- Go to the Amazon Web Services home page.
- Choose Sign Up. (Note: If you've signed in to AWS recently, it might say Sign In to the Console.)
- Type the requested account information, and then choose Continue. (Note: If Create a new AWS account isn't visible, first choose Sign in to a different account, and then choose to Create a new AWS account. When creating a new account, be sure that you enter your account information correctly, especially your email address. If you enter your email address incorrectly, you might not be able to access your account or change your password in the future.)
- Choose Personal or Professional. (Note: These two account types are identical in functionality.)
- Type the requested company or personal information.
- Read the AWS Customer Agreement, and then check the box.
- Choose Create Account and Continue.
Note: After you receive an email to confirm that your account is created, you can sign in to your new account using the email address and password you supplied. However, you must continue with the activation process before you can use AWS services.
Add a payment method:
On the Payment Information page, type the requested information associated with your payment method. If the address for your payment method is the same as the address you provided for your account, choose Secure Submit.
Otherwise, choose to Use a new address, type the billing address for your payment method, and then choose Secure Submit.
Verify your phone number:
- On the Phone Verification page, type a phone number that you can use to accept incoming phone calls.
- Enter the code displayed in the captcha.
- When you're ready to receive a call, choose to Call me now. In a few moments, an automated system will call you.
- Type the provided PIN on your phone's keypad. After the process is complete, choose Continue.
Next Topic: AMAZON COMPUTE SERVICES
Sunday, March 3, 2019
Online-Courses
March 03, 2019
Introduction to AWS?
This AWS tutorial for beginners is for absolutely anyone seeking to learn the basics of Amazon Web Services (AWS). we’ll guide you through the fundamentals of cloud computing until you become more confident with the AWS concepts and terminology.
- What is the cloud?
- What is AWS?
- What are AWS's core services?
In simple words AWS allows you to do the following things-
- Running web and application servers in the cloud to host dynamic websites.
- Securely store all your files on the cloud so you can access them from anywhere.
- Using managed databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle or SQL Server to store information.
- Deliver static and dynamic files quickly around the world using a Content Delivery Network (CDN).
- Send bulk email to your customers.
What is the cloud?
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of computing power, database storage, applications, and other IT resources through a cloud services platform via the internet. Cloud storage involves storing data on multiple virtual servers that are generally hosted by third parties. It is quickly becoming the standard way for technology companies to access IT infrastructure, software and hardware resources.
Let
us have a look at the various benefits of the public cloud
- Cost Effectiveness
- Quick and Easy Set Up
- Optimization of Staffing Budgets
- No Maintenance
- No Long-Term Contracts
- Economies of Scale
- Agility
- Global in Minutes
- High Flexibility without Redundancy
- Maximum Uptime and Zero Risk Failure
What is AWS?
Amazon web Services, popularly known as AWS, is a comprehensive and secure cloud services platform provided by Amazon. The AWS Cloud or Amazon cloud offers a good range of infrastructure services, like storage options, computing power, networking and databases to businesses, helping them scale and grow. Amazon delivers its services on-demand with pay-as-you-go rating policy.
What are
AWS's core services?
- Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2)
- Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS)
- Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS)
- Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3)
- Amazon Aurora
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon CloudWatch
- Amazon DynamoDB
- Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS)
- AWS Identity and Access Management (AWS IAM)
- AWS Lambda
- Amazon Route 53
- Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC)
- Elastic Load Balancing
Learn: AWS Online Training
Friday, March 1, 2019
Cloud-Computing
March 01, 2019
What is Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store)?
Amazon Elastic Block Store is a cloud-based block storage system provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that is best used for storing persistent data.
What Are AWS EBS Volumes?
Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) could be a raw block-level storage service designed to be used with Amazon EC2 instances. when mounted to Amazon EC2 instances, Amazon EBS volumes is used like any different raw block device: they'll be formatted with a particular filing system, host operating systems and applications, and have snapshots or clones made of them.
Two Types of AWS EBS Volumes
- SSD-backed volumes
- HDD-backed volumes.
SSD-backed volumes:-
SSD-backed volumes are optimized for transactional workloads, wherever the quantity performs a lot of small read/write operations. The performance of such volumes is measured in IOPS (input/output operations per second).
AWS users enjoy the ability to create EBS volumes that range in size from 1 GB up to 1 TB, create snapshot backups, and to create volumes from snapshots with a couple of clicks, with optional encryption at no extra charge.
The following instances support instance store volumes that use solid state drives (SSD) to deliver high random I/O performance: C3, G2, I2, M3, R3, and X1.
HDD-backed volumes are designed for large sequential workloads where throughput is much more important (and the performance is measured with MiB/s). Each category has two subsets.
The following instances offer non-volatile memory express (NVMe) SSD instance store volumes: C5d, I3, F1, M5d,,
p3dn.24xlarge R5d, and z1d.
Amazon EBS security:-
Amazon EBS provides encryption for data at rest, both for volumes and snapshots, to help the IT team meet security and compliance requirements. You can use Amazon-managed encryption keys or create and manage keys with AWS Key Management Service.
5 Functions of AWS EBS Volumes You're Not Using
- RAID
- Tuning Amazon EBS Performance
- Increasing Amazon EBS Volume Size While in Use
- Amazon Cloud Watch Events for Amazon EBS
- Sharing Snapshots Across AWS Accounts